In this post [link] I talk about how Mikoto assigns vertices to a bone using the geometry of the triangle created in Metasequoia for bdef meshes without using anchors.
To help visualise which vertices will be bound to a bone I wrote a script that shows the zone of influence of each bone.
The Metasequoia Python API doesn’t have routines to create Primitive objects so rather than create an object in code this script requires a Primitive to be created in Metasequoia which it can copy.
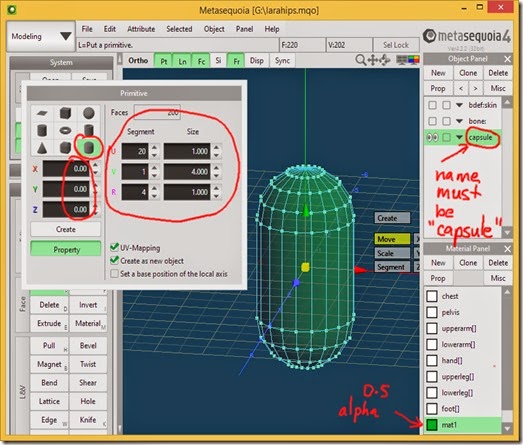
The Primitive object must be named capsule and have its properties set as shown in the screenshot below.
Note my tabs have been converted to one space indentation in the code below.
'''
Metasequoia Python script to show Mikoto bdef default bone influence
Only tested in version 4.2.2 trial
Before running the script:
1) an object named with "bone:" as the prefix and containing triangles must exist
2) an object named "capsule" with a material assigned to all faces must exist
3) create the "capsule" object using the Primitive in the right hand column and bottom row
4) the "capsule" object must be vertical
5) set the properties for the "capsule" object as:
X = 0, Y = 0, Z = 0
Segment Size
U 20 1
V 1 4
R 4 1
6) the material for the "capsule" object should have an alpha set to 0.5 to make it see through
7) the "capsule" object may be hidden and/or locked
After the script has finished a new object should have been created containing child objects
for each triangle in the "bone:" object showing the corresponding Mikoto bone's zone of influence
'''
# import Python's math module so its trigonometry functions and "pi" constant can be used
import math
# import Python's sys module so its "version_info" constant can be used
import sys
# global variables -> all functions can use them
doc = MQSystem.getDocument()
bone_obj = None
caps_obj = None
influence_object = None
# Metasequoia 4 -> can use print() or MQSystem.println() in scripts to print to output window
# Metasequoia 3 -> can only use MQSystem.println() in scripts to print to output window
def mqprint(message):
try:
print(message)
except:
MQSystem.println(str(message))
return
def ScalarTimesVec(scalar, vec):
outvec = MQSystem.newPoint(scalar*vec.x, scalar*vec.y, scalar*vec.z)
return outvec
def VecLength(vec):
return (vec.x*vec.x+vec.y*vec.y+vec.z*vec.z)**0.5
def RadToDegrees(angle):
return angle*180.0/math.pi
def RotPtAboutAxis(point, axis_pt, axis, angle):
'''
axis_pt is point on the axis
axis must be unit vector
angle in radians
source: https://sites.google.com/site/glennmurray/Home/rotation-matrices-and-formulas
'''
x, y, z = point.x, point.y, point.z
a, b, c = axis_pt.x, axis_pt.y, axis_pt.z
u, v, w = axis.x, axis.y, axis.z
theta = angle
t = 1 - math.cos(theta)
ct = math.cos(theta)
st = math.sin(theta)
x1 = (a*(v*v+w*w)-u*(b*v+c*w-u*x-v*y-w*z))*t+x*ct+(-c*v+b*w-w*y+v*z)*st
y1 = (b*(u*u+w*w)-v*(a*u+c*w-u*x-v*y-w*z))*t+y*ct+( c*u-a*w+w*x-u*z)*st
z1 = (c*(u*u+v*v)-w*(a*u+b*v-u*x-v*y-w*z))*t+z*ct+(-b*u+a*v-v*x+u*y)*st
return MQSystem.newPoint(x1,y1,z1)
def getCapsuleMat():
'''This function returns material index used for first face in "capsule" object'''
return caps_obj.face[0].material
def getData(f, obj):
'''This function returns length of short side, length of long side, direction
of long side and middle of long side of a "bone:" object triangle'''
result = {} # empty dictionary to store results
if f.numVertex == 3:
a = obj.vertex[f.index[0]]
b = obj.vertex[f.index[1]]
c = obj.vertex[f.index[2]]
vectors = [] # empty list to store vectors
vectors.append(b.pos - a.pos) # a -> b
vectors.append(c.pos - b.pos) # b -> c
vectors.append(c.pos - a.pos) # a -> c
#mqprint(vectors)
sides = [] # empty list to store lengths of sides
for v in vectors:
sides.append(VecLength(v))
i = 0
for s in sides:
if s == max(sides):
h_index = i # longest side
elif s == min(sides):
s_index = i # shortest side
else:
l_index = i # long side
i += 1
# find root vertex opposite longest side
if h_index == 0:
root = c.pos
elif h_index == 1:
root = a.pos
else:
root = b.pos
# find tip vertex opposite shortest side
if s_index == 0:
tip = c.pos
elif s_index == 1:
tip = a.pos
else:
tip = b.pos
direction = tip - root
#mqprint(direction)
centre = root + ScalarTimesVec(0.5, (direction))
# make direction a unit vector
direction.normalize()
result["direction"] = direction
result["long"] = sides[l_index]
result["short"] = sides[s_index]
result["centre"] = centre
return result
else:
return result
def drawCapsule(parent_obj, radius, length, centre, direction):
'''This function creates a copy of the "capsule" object, scales it according to the short side
of a "bone:" object triangle and aligns it with the long side of a "bone:" object triangle'''
#mqprint("R %f, L %f, C %s, D %s"%(radius, length, str(centre), str(direction)))
obj = MQSystem.newObject()
R_size = 1.0 # "capsule" object R size
ratio = radius/R_size # scale radius to short side length
svector = MQSystem.newPoint(ratio,ratio,ratio)
rvector = MQSystem.newAngle()
tvector = MQSystem.newPoint()
SRTmatrix = MQSystem.newMatrix()
SRTmatrix.setTransform(svector, rvector, tvector)
# scale the capsule in all axes
for v in caps_obj.vertex:
obj.addVertex(SRTmatrix.mult(v.pos))
for f in caps_obj.face:
obj.addFace(list(f.index))
# move vertices of the capsule in vertical (Y) axis
for v in obj.vertex:
if v.pos.y > 0:
v.pos.y -= (1*ratio - length/2.0)
else:
v.pos.y += (1*ratio - length/2.0)
capsule_vec = MQSystem.newPoint(0.0,1.0,0.0) # capsule object axis unit vector
rot_axis = capsule_vec.crossProduct(direction) # axis perpendicular to the two vectors
rot_axis.normalize()
#mqprint(rot_axis)
cosTheta = capsule_vec.dotProduct(direction) # cosine of angle between the two unit vectors
if cosTheta > 1.0:
cosTheta = 1.0
if cosTheta < -1.0:
cosTheta = -1.0
rot_angle = math.acos(cosTheta) # rot_angle in radians
#mqprint(RadToDegrees(rot_angle)) # always positive
axis_pt = MQSystem.newPoint()
for v in obj.vertex:
v.setPos(RotPtAboutAxis(v.pos, axis_pt, rot_axis, rot_angle))
svector = MQSystem.newPoint(1.0, 1.0, 1.0)
rvector = MQSystem.newAngle()
tvector = MQSystem.newPoint(centre.x, centre.y, centre.z)
# translate capsule centre to middle of long side
SRTmatrix.setTransform(svector, rvector, tvector)
for v in obj.vertex:
v.pos = SRTmatrix.mult(v.pos)
# assign capsule material to created object
mat = getCapsuleMat()
for f in obj.face:
f.material = mat
if not (doc.material[mat].alpha < 1.0):
doc.material[mat].alpha = 0.5
# add object to document
idx = doc.addObject(obj, parent_obj)
return
def main():
'''
Write the script as a function so can stop the script by using a "return"
statement if necessary to exit the function.
It is not required to name this function "main".
'''
if doc.numObject == 0:
mqprint("No objects")
return
# make this function use the global variables and not create local variables with the same
# names because these names appear on the left hand side of an assignment (=) statement
global caps_obj
global bone_obj
global influence_object
for ob in doc.object:
if ob == None:
continue
if ob.name.startswith("bone:"):
bone_obj = ob
if ob.name.lower() == "capsule":
caps_obj = ob
if bone_obj == None:
mqprint('No "bone:" object found')
return
if caps_obj == None:
mqprint('No "capsule" object found')
return
if bone_obj.numFace == 0:
mqprint('No faces in "bone:" object')
return
count = 0
for f in bone_obj.face:
if f.numVertex == 3:
count += 1
if count == 0:
mqprint('No triangles in "bone:" object')
return
if caps_obj.numFace == 0:
mqprint('No faces in "capsule" object')
return
obj = MQSystem.newObject()
idx = doc.addObject(obj)
influence_object = doc.object[idx]
# make the object the current object
doc.currentObjectIndex = idx
for f in bone_obj.face:
if f.numVertex != 3:
continue
data = getData(f, bone_obj)
if data:
drawCapsule(influence_object, data["short"], data["long"], data["centre"], data["direction"])
else:
mqprint("No data for face %d"%(f.id))
return
'''
If this script is executed (Run) its __name__ variable is the string "__main__" and the
statements in the following "if" block execute but if this script is imported into
another script its __name__ variable is not "__main__" so the "if" block statements
will not be executed
'''
if __name__ == "__main__":
# clear the Metasequoia Script Editor output window each time before the script is run
MQSystem.clearLog()
# print Python major.minor.revision version
# Metasequoia 3 uses Python 2.*, Metasequoia 4 uses Python 3.*
mqprint("Python version is %d.%d.%d"%(sys.version_info[0], sys.version_info[1], sys.version_info[2]))
# call the function "main()" to execute its code
main()
# let user know script has finished
mqprint("Script finished")
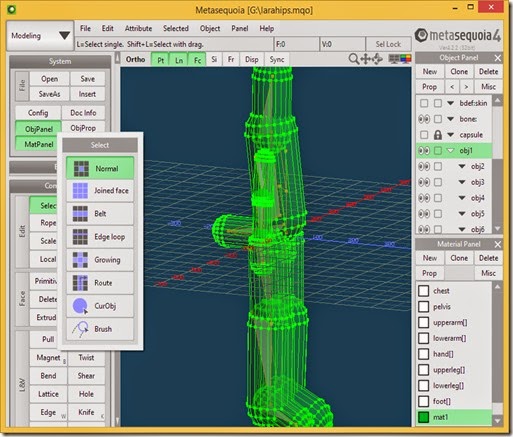
Below is a screenshot showing the skeleton in Metasequoia before running the script.

Below is a screenshot after running the script showing the zone of influence for the triangles of the skeleton.
No comments:
Post a Comment